A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, depriving brain cells of oxygen and nutrients, leading to damage. Strokes can have life-altering consequences, making it crucial to recognize the signs early, seek immediate treatment, and provide long-term support for recovery.
What Is a Stroke?
There are two main types of strokes:
• Ischemic Stroke: The most common type, caused by a blood clot blocking a vessel in the brain.
• Hemorrhagic Stroke: Caused by a burst blood vessel leading to bleeding in or around the brain.
Both types of strokes cause brain cells to die rapidly, making prompt medical intervention critical for minimizing damage.
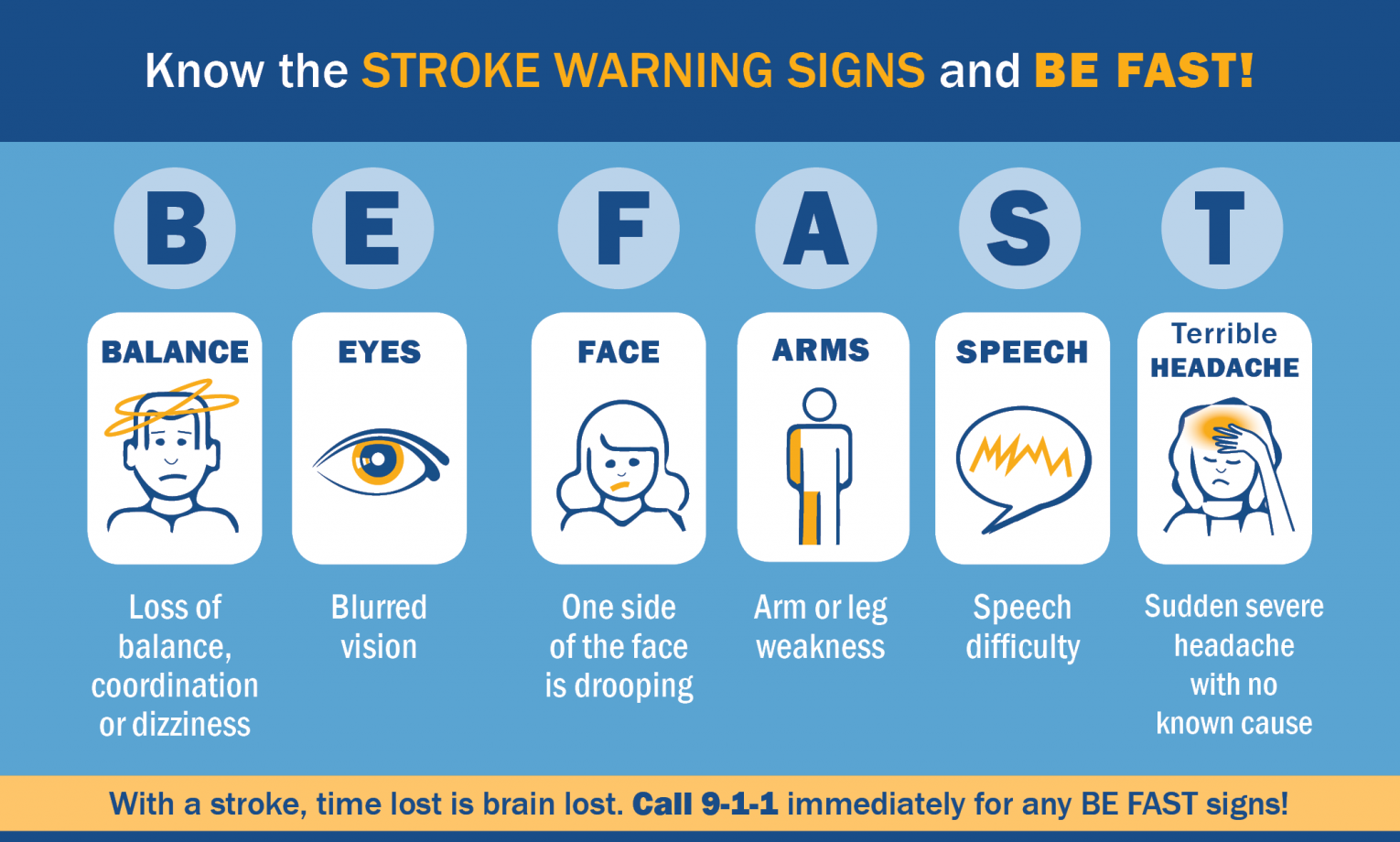
How to Identify a Stroke: F.A.S.T.
Recognizing the early signs of a stroke can save lives. The acronym F.A.S.T. is an easy way to remember the warning signs:
• F – Face Drooping: Is one side of the face numb or drooping? Ask the person to smile; is it uneven?
• A – Arm Weakness: Is one arm weak or numb? Ask the person to raise both arms; does one drift downward?
• S – Speech Difficulty: Is speech slurred, or are they unable to speak? Ask them to repeat a simple sentence.
• T – Time to Call 911: If you notice any of these signs, call 911 immediately. Time is critical in preventing long-term damage.
Other possible stroke symptoms include sudden confusion, vision problems, dizziness, or a severe headache with no known cause.
Immediate Treatment for Stroke
A stroke is a medical emergency that requires urgent attention. Treatment depends on the type of stroke:
• For Ischemic Stroke: A clot-busting drug called tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is used to dissolve clots and restore blood flow. This treatment must be administered within a 3-4.5 hour window for maximum effectiveness.
• For Hemorrhagic Stroke: Treatment involves stopping the bleeding and relieving pressure in the brain. This may require surgery or other interventions to repair damaged blood vessels.
In both cases, fast action is crucial. The sooner treatment begins, the better the chances of recovery.
Helping Patients After a Stroke
Recovery from a stroke can be a long process, but there are several ways to support patients during rehabilitation:
1. Physical Therapy: Many stroke survivors experience weakness or paralysis, especially on one side of the body. Physical therapy helps patients regain strength, balance, and coordination.
2. Speech Therapy: A stroke can affect speech and language skills. Speech therapists work with patients to restore their ability to communicate effectively.
3. Occupational Therapy: Stroke survivors may need help relearning everyday activities like dressing, eating, and using utensils. Occupational therapists provide strategies to help them regain independence.
4. Emotional Support: Depression and anxiety are common after a stroke. Providing emotional support and, if necessary, seeking counseling or support groups can help stroke survivors cope with the emotional challenges of recovery.
5. Healthy Lifestyle Changes: Encouraging patients to adopt a healthier lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking, can reduce the risk of a second stroke.
Preventing Future Strokes
Once a patient has experienced a stroke, the risk of another one increases. Preventive measures include:
• Managing High Blood Pressure: Controlling hypertension is one of the most effective ways to reduce stroke risk.
• Lowering Cholesterol: Reducing cholesterol levels can help prevent future blockages in blood vessels.
• Blood Thinners: For those at risk of clot formation, doctors may prescribe anticoagulant medications to reduce the likelihood of blood clots forming.
• Maintaining a Heart-Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while minimizing processed foods can improve overall cardiovascular health.
• Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, lower blood pressure, and improve overall heart health.
Conclusion
A stroke can be a life-changing event, but with the right knowledge and timely intervention, it is possible to prevent severe damage and improve outcomes. Recognizing the signs of a stroke, seeking immediate treatment, and providing comprehensive rehabilitation are all vital steps in helping stroke survivors reclaim their lives. Understanding these principles can make a difference in saving lives and supporting those affected by stroke.